The nuclear lamina is a network of filaments composed of proteins called lamins that underlies the nuclear membrane. The nuclear lamina plays essential roles in nuclear architecture, positioning of nuclear pores, gene expression regulation, chromatin organization, DNA replication, and DNA repair.
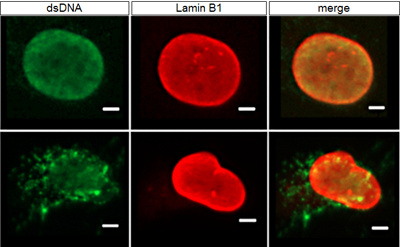
Mutations in genes involved in the expression or processing of lamins cause genetic disorders known as laminopathies. For instance, mutations in the LMNA or ZMPSTE24 genes can lead to the accumulation of incompletely processed forms of lamin A that localize to the inner nuclear membrane instead of the nuclear lamina, where normal mature lamin A resides. Mislocalized lamins profoundly disrupt nuclear function and structure, often resulting in nuclear blebbing. In severe cases, nuclear rupture can occur, causing a loss of compartmentalization and leakage of genomic DNA into the cytosol.
Courtesy: Alannah DiCintio
A technique that allows monitoring of nuclear integrity in human cells could enhance the study of potential treatments for eliminating or significantly improving disease phenotypes. In their new study titled "Detection of Nuclear Blebbing and DNA Leakage in Mammalian Cells by Immunofluorescence", graduate student Alannah DiCintio, former graduate student Liza Joudeh, and their mentor Dr. Alan Waldman, employed specific antibodies against a lamin protein and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) to simultaneously visualize the nuclear envelope and DNA. By enabling a rapid assessment of nuclear structural integrity and the potential leakage of nuclear DNA into the cytosol, this approach broadens our understanding of the characteristics of laminopathies and can be used to evaluate the efficacy of potential treatments for disorders of the nucleus.